Application methods / Coating rotoling
Coating rotoling
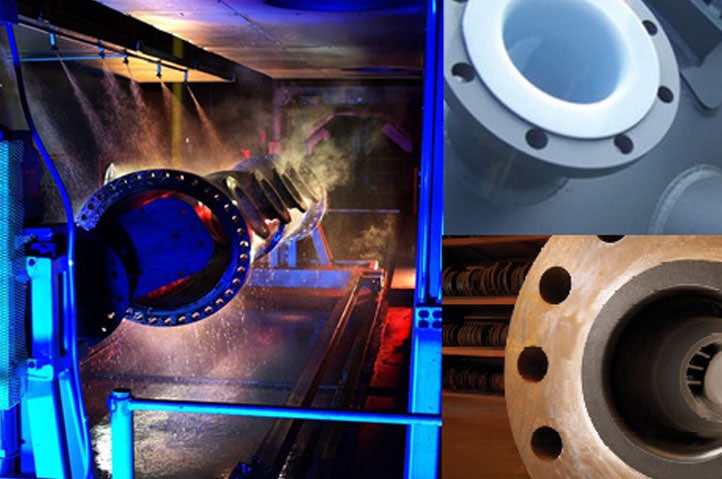

It is a technology for bonding thermoplastic polymers inside tanks, vessels, pipes, fittings and other types of process equipment.
The resulting polymer layer adds corrosion protection and resistance to chemicals.
Rotolining is applied by means of a rotational process. Workers place the granular powder resin inside the container or similar process equipment; they seal all its openings and then mount the container inside an oven.
The oven rotates on two perpendicular axes at low speed, giving the resin time to melt and spread evenly over all internal surfaces of the equipment. The rotation of the oven causes the polymer to adapt to the internal shape of the vessel.
The processed equipment is cooled slowly to prevent shrinkage and deformation. After cooling, the polymer provides a continuous, permanently bonded coating.
Depending on the polymer used and the service application of the equipment, the thickness of a rotational coating varies from 0.23 cm to 2.5 cm.
Such a thick coating provides greater protection against corrosion and abrasion, maximising the life of the equipment.
